Friends or Foes: Will 5G Replace WiFi?
Thanks to 5G technology, mobile data has become just as efficient for a strong internet connection as our home networks. After all, it’s even faster than cable internet! All you need is a 5G-ready mobile phone and a 5G tower nearby. Say goodbye to routers, cables, and even broadband infrastructure. Because of this, many have started wondering why we even need our home WiFi networks. Will 5G replace WiFi?
Well, not quite. After all, 5G is not a WiFi replacement but a completely different technology with similar benefits. This blog post explains what 5G is and how it compares to home WiFi networks. Keep reading to find out more!

5G vs WiFi: What’s the Difference?
Before we start, we first need to go over some common WiFi terms to help understand whether 5G will replace WiFi. Below, we explain what WiFi and 5G are, outlining their pros and cons.
What is WiFi?
WiFi means a wireless networking technology: a version of WLAN technology. It allows users to receive wireless signals from their routers and connect to the internet. WiFi connects to your devices using radio waves. Typically, one household shares a single WiFi network.
As you might understand from your home network, WiFi has a limited range. The farther you are from the router, the weaker the signal will be. This can result in lagging or connection dropping. Therefore, it’s not optimal to use WiFi outdoors or if you’re on the move.
The newest generation is WiFi 6, also known as 802.11ax WiFi. With a new router, it can reach up to 10 Gbps speed.
What is 5G?
5G stands for 5th generation of broadband cellular communications, each generation being faster than the earlier one. It first entered our lives in 2019. The 5G network has enough capacity to connect vast amounts of devices, including Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Machine to Machine (M2M) systems. Additionally, 5G technology supports bandwidth-heavy activities, such as exploring immersive digital VR worlds, augmented reality, and industrial automation.
Unlike WiFi, users can connect to 5G anywhere there’s a signal. They can turn on mobile data and instantly enjoy high internet speeds, regardless of the router’s location and other challenges that otherwise slow down the internet.
Compared to 4G and its forebearers, 5G supplies the following benefits:
- Multi-gigabit speeds (100 times faster than 4G)
- Higher maximum upload and download speeds (minimum speeds of 20 Gbps)
- Higher traffic volumes
- Low latency, which means no perceivable lagging
- Wider bandwidth with higher frequency spectrums
- Reliable internet in areas without broadband infrastructure, bridging the digital divide
- Potential to service 8.4 million homes in rural areas
- Potential for new and improved technologies, such as smart home devices, AI machinery, and cloud storage
The figure below shows what applications of 5G consumers are most excited about, according to IBM’s 2019 study, What Consumers Expect from 5G Entertainment.
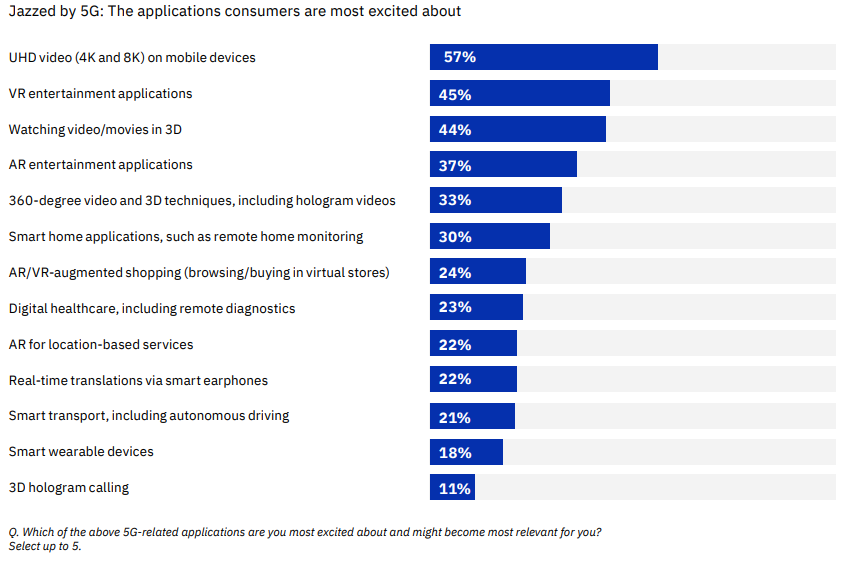
Source: IBM
However, the new 5G technology also has its drawbacks.
- New cybersecurity risks. New software means new points of entry for cybercriminals. We will need to learn new ways of protecting our personal information online.
- More cyberattacks. 5G promises higher connectivity, but with more devices connected to the internet, there’s an even higher risk of cyberattacks.
- The rollout is slow despite all the potential 5G holds. 5G can improve connectivity in rural areas, but it’s much easier to set up transmitters in cities with higher buildings. Therefore, the digital divide could temporarily grow larger.
Will 5G Replace WiFi?
So, the question remains: will 5G replace WiFi? The simple and short answer is no.
As explained above, 5G is a cellular technology and WiFi is a wireless LAN technology. They’re two different technologies that are in no way competing. You can typically find WiFi in indoor spaces or set locations, but you can connect to 5G anywhere.
But they have some shared goals, namely higher internet speeds and bandwidth. Each with its benefits, they can bridge the digital divide to form a better broadband infrastructure for a better-connected tomorrow.
5G and WiFi currently co-exist. For example, if you turn on your mobile data and WiFi, your smartphone will automatically connect to the source that provides a better service. In the upcoming years, we can expect to see 5G and WiFi converging in new ways.

Conclusion: 5G Won’t Replace WiFi (Yet!)
The world we’re living in is more connected with every passing year, thanks to new technologies, such as 5G. But will 5G replace WiFi, the network technology we all use in our daily lives? We don’t think so.
5G and WiFi are not mutually exclusive technologies, and they both have their sets of pros and cons.
While it’s too early to tell how the relationship between 5G and WiFi will work out in the long run, it’s safe to say that 5G won’t replace WiFi. Together, they’ll enable us to connect to more devices, enjoy higher internet speeds, and spend more time in VR worlds.
One thing is certain: slow internet will soon be a thing of the past. At Race Communications, we’re dedicated to bringing fast and reliable gigabit internet to all communities in California and beyond. If you’re interested in our services, contact our specialists at 877-722-3833 or send us an inquiry.


